Approximately 1,900 Citrix networking products worldwide have been compromised in a large-scale automated campaign targeting a specific vulnerability, according to researchers from Fox-IT, a part of NCC Group. The attackers took advantage of CVE-2023-3519 to establish persistence by exploiting vulnerable Citrix NetScaler Application Delivery Controllers (ADC) and Citrix NetScaler Gateways, and placing Web shells on them.
The presence of the Web shell gives the adversary the ability to remotely execute arbitrary commands even after the affected appliance has been updated or rebooted. Last month, when the vulnerability was first disclosed and a patch was released, researchers from Mandiant identified over half a dozen Web shells being used by attackers to modify the NetScaler configuration, as well as stop or deactivate processes and services.
According to Mandiant researchers, cyber espionage threat actors have been focusing on edge devices, particularly security, networking, and virtualization technologies since at least 2021. This enables them to gain persistent access to victim networks while evading detection.
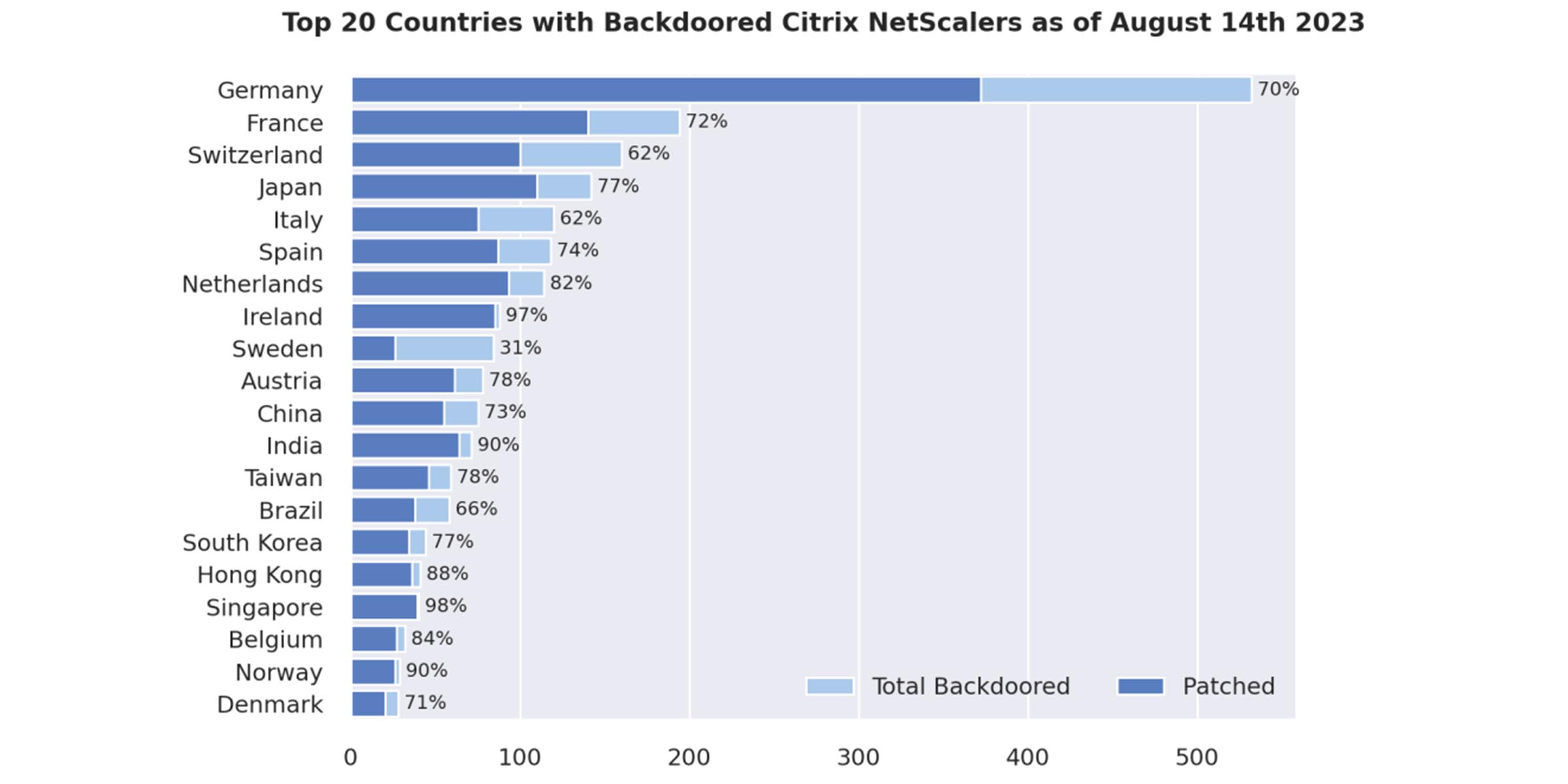
During the automated campaign, which Fox-IT researchers estimate took place between July 20 and July 21, around 31,127 NetScalers were vulnerable to the remote code execution flaw associated with CVE-2023-3519. As of August 14, nearly 1,900 NetScalers have been found to have some form of backdoor. Out of the compromised systems, 1,248 had already been patched for this particular vulnerability.
However, despite most administrators being aware of the vulnerability and patching their NetScalers, there hasn’t been thorough verification to ensure that successful exploitation hasn’t taken place. Fox-IT warns that simply updating and rebooting the system is insufficient in this case. Enterprise defenders should still check their NetScalers for signs of compromise, regardless of when the patch was applied. Mandiant’s IoC Scanner, a bash script designed to check for indicators of compromise on NetScaler appliances, can be employed for this purpose.
If a Web shell is discovered, defenders can further investigate by examining the NetScaler access logs to determine whether it was used. If there are indications of this, it becomes necessary to identify whether the adversary has moved laterally within the network.
The majority of compromised NetScalers appear to be located in Europe. While Canada, Russia, and the United States had thousands of vulnerable NetScalers on July 21, Fox-IT reports that there were virtually no installations with Web shells in these countries.
Mandiant’s researchers note that this campaign aligns with previous operations carried out by suspected espionage threat actors linked to China, based on their research from last year when similar appliances were targeted. Over the years, Mandiant has investigated numerous intrusions at defense industrial base, government, technology, and telecommunications organizations where China-nexus groups were suspected of exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities and employing custom malware to steal user credentials and maintain lasting access to victim environments.
It is imperative for organizations to remain vigilant and take appropriate measures to secure their Citrix NetScaler appliances, as these ongoing attacks continue to pose a significant threat to network security.