A critical security issue known as Fast Flux has been brought to light in a joint advisory by international cybersecurity agencies, including the National Security Agency (NSA), Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), Australian Signals Directorate’s Australian Cyber Security Centre (ASD’s ACSC), Canadian Centre for Cyber Security (CCCS), and New Zealand National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC-NZ). The advisory points out that both cybercriminals and state-sponsored actors are taking advantage of this new technique, which allows them to hide malicious server locations and maintain persistent command and control (C2) infrastructure, labeling it as a national security threat.
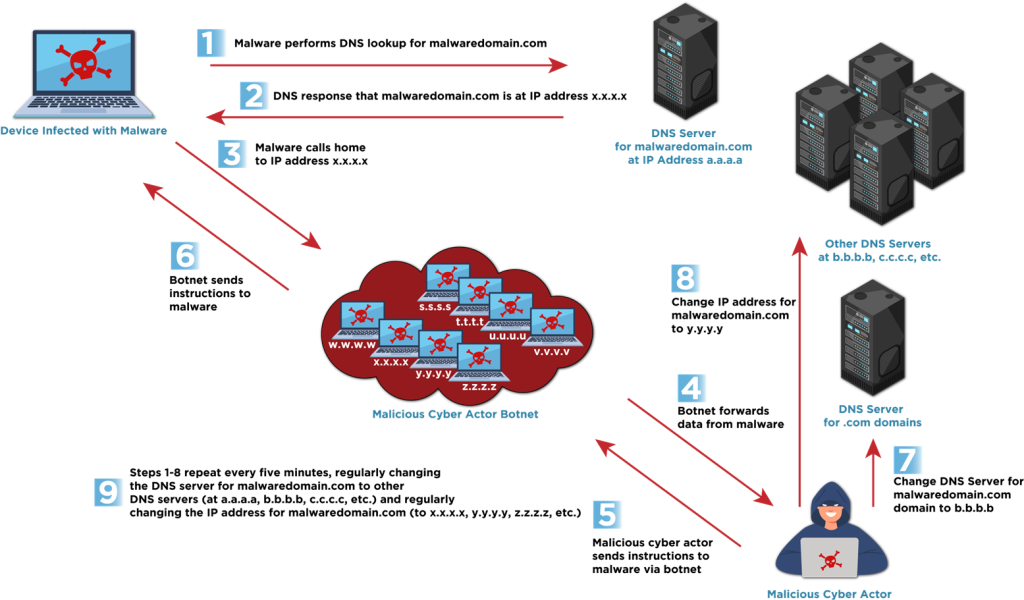
Fast flux operates through the dynamic manipulation of Domain Name System (DNS) records, rapidly changing the IP addresses associated with a single domain to confuse the true location of malicious servers. This constant rotation renders traditional IP-based blocking methods ineffective, making it challenging to combat this evolving threat. Cybercriminals are employing two methods of fast flux – Single flux and Double flux. Single flux involves linking a single domain name to multiple frequently rotated IP addresses, ensuring access even if one IP is blocked. On the other hand, Double flux takes it a step further by frequently changing the DNS name servers along with the IP addresses, adding an additional layer of anonymity.
These techniques utilize compromised hosts to create botnets, acting as proxies to mask the origin of malicious traffic. Fast Flux proves beneficial beyond C2 communications, playing a pivotal role in phishing campaigns and making social engineering websites resistant to takedown efforts. Bulletproof hosting (BPH) providers, known for disregarding law enforcement requests, offer this service to clients for running illicit operations like botnet management, fake online shops, and credential theft. This enables cybercriminal activities to thrive while evading detection and shutdown, as witnessed in attacks like Hive and Nefilim ransomware incidents.
Detection and mitigation strategies recommended by the agencies involve a multi-layered approach, utilizing threat intelligence feeds, anomaly detection for DNS query logs, analysis of DNS record time-to-live (TTL) values, monitoring for inconsistent geolocation, and flow data analysis to identify unusual communication patterns. Organizations are advised to implement DNS and IP blocking, reputational filtering, enhanced monitoring and logging, and phishing awareness training to counter the threats posed by fast flux. Collaboration with Internet service providers and cybersecurity providers, especially Protective DNS (PDNS) providers, is crucial to successfully implement these measures.
John DiLullo, CEO at Deepwatch, a San Francisco AI+Human Cyber Resilience Platform, expressed his views on the advisory, emphasizing the significance of correlative detection techniques in combating such intrusions. He highlighted the importance of leveraging ‘low and slow’ Machine Learning methods to outsmart these exploits, stressing the need for organizations to enhance their infrastructure security measures in response to this wake-up call. This latest development serves as a reminder for enterprises to reassess their security protocols and adopt advanced detection and mitigation strategies to safeguard against fast flux threats.